Introduction
Exploring the world of cannabinoids reveals a diverse array of compounds, each with its unique properties and potential benefits. Among the lesser-known cannabinoids gaining attention are Delta-10 (Δ10) and Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the differences between Delta-10 and THCV, exploring their chemical structures, potential effects, and emerging research.
Delta-10 (Δ10)
Delta-10 is a relatively new addition to the cannabinoid family, joining the more well-known compounds such as Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Like other cannabinoids, Delta-10 interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters involved in maintaining homeostasis in the body.
Chemical Structure
Delta-10, similar to Delta-9-THC, belongs to the group of tetrahydrocannabinols. The chemical structure of Delta-10 includes a chain of carbon atoms forming a ring, known as a cyclohexene ring, with side chains and functional groups. This structure influences how Delta-10 interacts with the cannabinoid receptors in the ECS.
Origin and Extraction
Delta-10 is derived from the hemp plant, just like Delta-9-THC and CBD. It can be found in trace amounts in cannabis strains, but its concentration is typically much lower compared to Delta-9-THC or CBD. Extraction methods, including distillation and isolation processes, are used to concentrate and purify Delta-10 for various products.
Potential Effects
Research on Delta-10 is still in its early stages, and the available information is limited. However, anecdotal reports suggest that Delta-10 may offer a milder psychoactive experience compared to Delta-9-THC. Some users describe feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and increased focus. Like other cannabinoids, the effects of Delta-10 can vary between individuals.
THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)
THCV is a cannabinoid that shares a similar precursor with THC (Delta-9-THC) but has a different chemical structure and distinct effects. It is found in varying concentrations in different cannabis strains, and its potential therapeutic properties are a subject of growing interest.
Chemical Structure
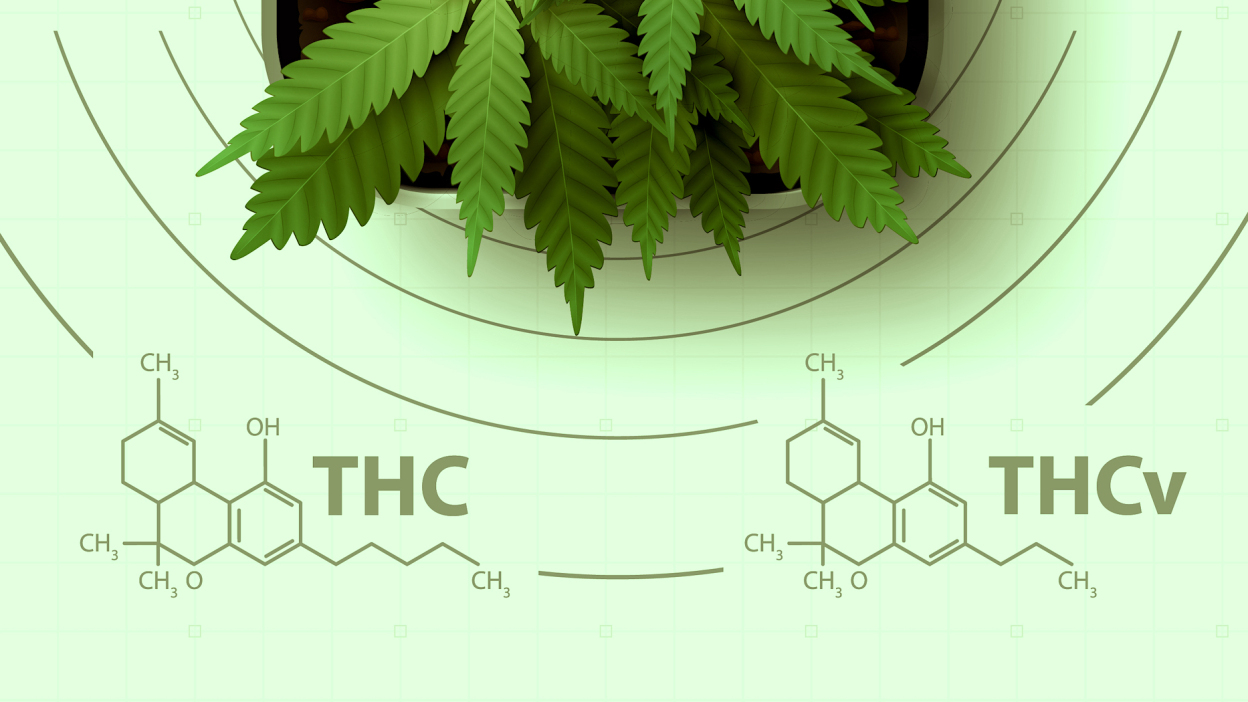
THCV differs from THC in its chemical structure, primarily in the length of its alkyl side chain. This structural difference influences its binding affinity to cannabinoid receptors, particularly CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS. THCV is a propyl cannabinoid, while THC is a pentyl cannabinoid.
Origin and Extraction
THCV is naturally present in cannabis plants, with varying concentrations depending on the strain. It is more commonly found in sativa strains, particularly those indigenous to regions like Africa and Southeast Asia. Similar to other cannabinoids, THCV can be extracted and isolated for use in various products.
Potential Effects
THCV is known for its unique effects, distinct from those of THC. While the research is ongoing, some potential effects of THCV include:
- Appetite Suppression: Unlike THC, which is often associated with an increase in appetite (the “munchies”), THCV may have appetite-suppressant properties. This has led to interest in its potential use for weight management.
- Energizing and Focus: THCV has been reported to have energizing and focus-enhancing effects. Some users describe increased mental clarity and alertness without the sedative effects associated with certain cannabis strains.
- Potential Antiepileptic Properties: There is preliminary research suggesting that THCV may have antiepileptic properties, making it a subject of interest in the study of epilepsy and seizure disorders.
- Bone Health: Some studies have explored the potential role of THCV in promoting bone health and preventing osteoporosis. Research in this area is still in the early stages.
- Neuroprotective Effects: THCV has demonstrated neuroprotective properties in preclinical studies, suggesting a potential role in protecting the brain from damage associated with conditions such as Parkinson’s disease
Differences Between Delta-10 and THCV
Chemical Structure
- Delta-10 is a tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) with a cyclohexene ring structure, similar to Delta-9-THC but with subtle differences.
- THCV is a propyl cannabinoid with a different chemical structure from both Delta-9-THC and Delta-10, characterized by a propyl side chain instead of a pentyl side chain.
Psychoactive Effects
- Delta-10 is reported to have mild psychoactive effects, with users describing feelings of euphoria and relaxation. The intensity of its psychoactivity appears to be less than that of Delta-9-THC.
- THCV may have a unique set of effects, including appetite suppression, increased energy, and focus. It is not typically associated with the same level of psychoactivity as Delta-9-THC.
Appetite Effects
- Delta-10 does not have well-documented effects on appetite and is not known for its impact on hunger.
- THCV is known for its potential appetite-suppressant effects, making it a subject of interest in weight management.
Strain Specificity
- Delta-10 can be found in trace amounts in various cannabis strains but is not as well-documented as Delta-9-THC or CBD.
- THCV is present in varying concentrations in different cannabis strains, with higher levels often found in sativa strains.
Therapeutic Potential
- Delta-10 is still in the early stages of research, and its therapeutic potential is not well-established. Anecdotal reports suggest potential benefits, but more studies are needed.
- THCV has been studied for various potential therapeutic properties, including appetite suppression, neuroprotection, and potential antiepileptic effects. However, research is ongoing, and further investigation is needed to fully understand its therapeutic potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Delta-10 and THCV are two distinct cannabinoids with unique chemical structures and potential effects. Delta-10, a relatively recent discovery, is still being explored for its properties and potential benefits, while THCV has garnered attention for its specific effects, including appetite suppression and potential therapeutic applications. As with any cannabinoids, individual responses can vary, and further research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential. Before incorporating Delta-10, THCV, or any cannabinoid into your wellness routine, it’s advisable to consult with healthcare professionals and consider the legal status of these compounds in your region.
- The Ultimate Review of the Top Vape Pens By Head Shop - August 21, 2024
- What’S The Difference Between Delta 10 And Thcv - November 9, 2023
- Benefits of Lions Mane Functional Mushrooms - November 9, 2023